Micro Incision Topical phaco
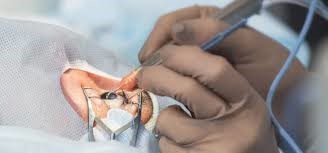
Introduction
Micro Incision Topical Phacoemulsification, often referred to as MICS, represents a significant advancement in cataract surgery. This technique combines the benefits of smaller surgical incisions with the use of topical anesthesia, resulting in a less invasive procedure with a quicker recovery time and reduced complications.
Understanding Micro Incision Surgery
Micro incision surgery involves creating very small incisions, typically less than 2.2 mm, compared to the larger incisions used in traditional phacoemulsification. These tiny incisions facilitate a less invasive approach, which reduces trauma to the eye, speeds up healing, and minimizes the risk of postoperative complications such as infection and astigmatism.
Phacoemulsification Technique
Phacoemulsification, or phaco, is a modern cataract surgery technique that uses ultrasound waves to emulsify the eye’s cloudy lens, which is then aspirated out through the small incision. The micro incision approach enhances this technique by allowing the use of even finer instruments, which improves surgical precision and outcomes.
Topical Anesthesia
One of the key components of Micro Incision Topical Phaco is the use of topical anesthesia instead of general or regional anesthesia. Topical anesthesia involves applying anesthetic eye drops to numb the eye’s surface, eliminating the need for injections around the eye. This approach reduces the risk of complications associated with injectable anesthesia and allows for a more comfortable and stress-free experience for the patient.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Preparation: The patient receives a series of anesthetic eye drops to numb the eye. Pupils are dilated using additional drops.
- Incision Creation: The surgeon makes a micro incision in the cornea using a precision blade or laser.
- Phacoemulsification: A phacoemulsification probe is inserted through the micro incision. Ultrasound waves break up the cataract, which is then suctioned out.
- Lens Insertion: An intraocular lens (IOL) is inserted through the same incision and positioned in the eye.
- Completion: The incision is usually self-sealing, eliminating the need for stitches. An antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drop is administered to prevent infection and reduce inflammation.
Advantages of Micro Incision Topical Phaco
- Minimally Invasive: The small incision size reduces trauma to the eye, leading to faster healing and less postoperative discomfort.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions lower the chances of infection and other complications.
- Faster Recovery: Patients often experience quicker visual recovery and can resume normal activities sooner.
- No Need for Stitches: The self-sealing nature of the micro incisions typically eliminates the need for sutures, further enhancing patient comfort.
- Enhanced Precision: The use of advanced phacoemulsification technology allows for greater surgical precision and better outcomes.
Patient Selection and Considerations
Micro Incision Topical Phaco is suitable for most patients with cataracts, but certain factors such as the presence of corneal abnormalities or other ocular conditions may influence the decision to use this technique. A thorough preoperative assessment is essential to determine the best surgical approach for each individual patient.
Postoperative Care
Following the procedure, patients are usually prescribed antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops to prevent infection and control inflammation. Regular follow-up visits are scheduled to monitor healing and visual outcomes. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities and follow specific care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery.
